We are studying fetal brain development based on in-utero magnetic resonance imaging data acquired from the 18th to 40th gestational week, with a focus on modelling structural- and functional changes during gestation.
Projects
Ongoing: FASD, TRABIT; Finished: FETAL4D, FETALMORPHO, FETLAS
Workshops, Challenges and Awards

The prenatal assessment of functional asymmetries in the developing human brain using in-utero fMRI, presented at FIT'NG 2022 on 5th of September 2022 by Athena Taymourtash received the FIT'NG Young Investigator Award!
We are Co-organisers of the FeTal brain Annotation and Segmentation (FeTA) Challenge since 2021. New this year: Multi-site generalization segmentation task with also data from the Medical University of Vienna! Check out the hybrid presentations on 18th of September during MICCAI 2022.
Highlight Publications
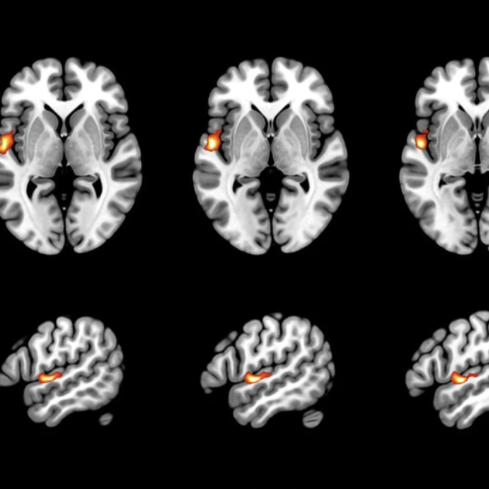
NEW PAPER: Fetal brain morphology as a predictor for language development. This study investigated the prognostic value of STS depth asymmetry in healthy fetuses for later language abilities, language localization, and language-related white matter tracts. Less right lateralization of the fetal STS depth was significantly associated with better verbal abilities, with fetal STS depth asymmetry explaining more than 40% of variance in verbal skills 6–13 years later. Furthermore, less right fetal STS depth asymmetry correlated with increased left language localization during childhood. (Lisa Bartha-Doering et al. Communications Biology 2023)
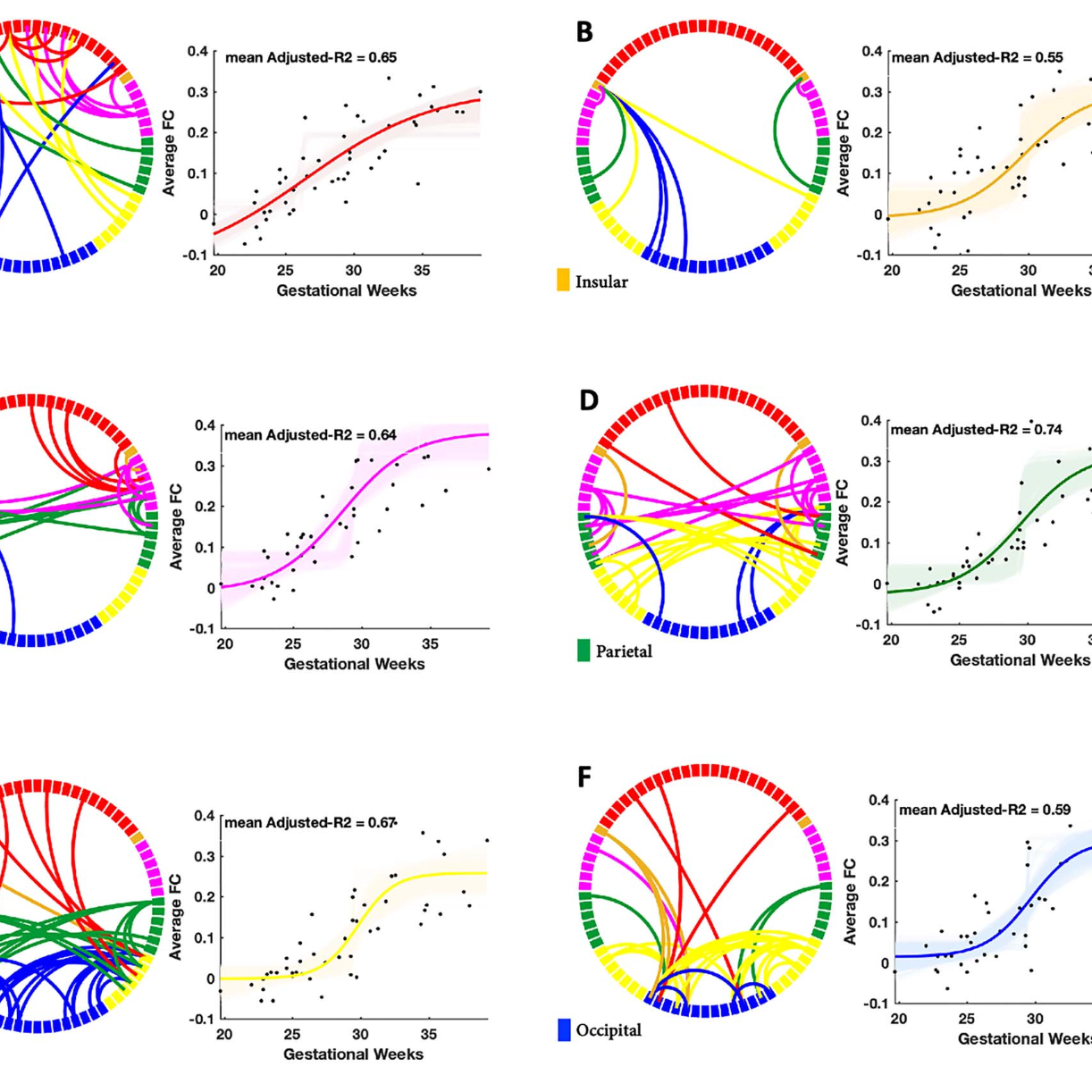
Fetal functional thalamo-cortical and cortico-cortical networks develop along specific trajectories. We modeled fetal functional thalamocortical connectome development using in-utero functional MRI in fetuses observed from 19th to 40th weeks of gestation. A peak increase of thalamo-cortical functional connectivity strength occurs between 29th and 31st GW, right before axons establish synapses in the cortex. The cortico-cortical connectivity increases in a similar time window, and exhibits significant functional laterality in temporal-superior, -medial, and -inferior areas. The similarity of homologous regions decreases during gestation giving way to a more diverse cortical interconnectedness. (Taymourtash et al. 2022 Cerebral Cortex)
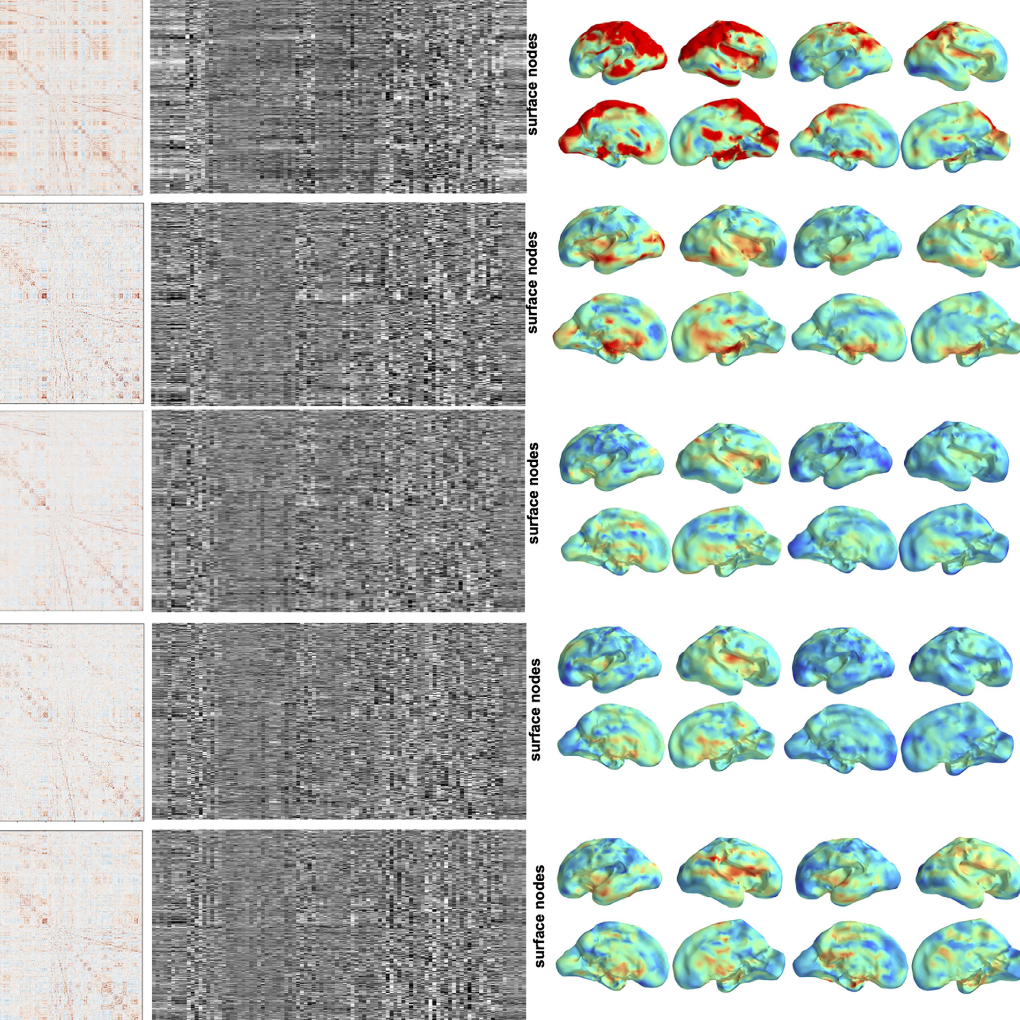
Motion correction and volumetric reconstruction for fetal functional magnetic resonance imaging data estimates a high-resolution reference volume by using outlier-robust motion correction, and utilizes Huber L2 regularization for intra-stack volumetric reconstruction of the motion-corrected fetal brain fMRI. (Sobotka et al. 2022 Neuroimage).
Spatio-temporal motion correction using iterative reconstruction of in-utero fetal fMRI. 4D low-rank regularization can reconstruct the entire time series at once and exploits relationships within, and across time frames (Taymourtash et al. 2022 MICCAI)
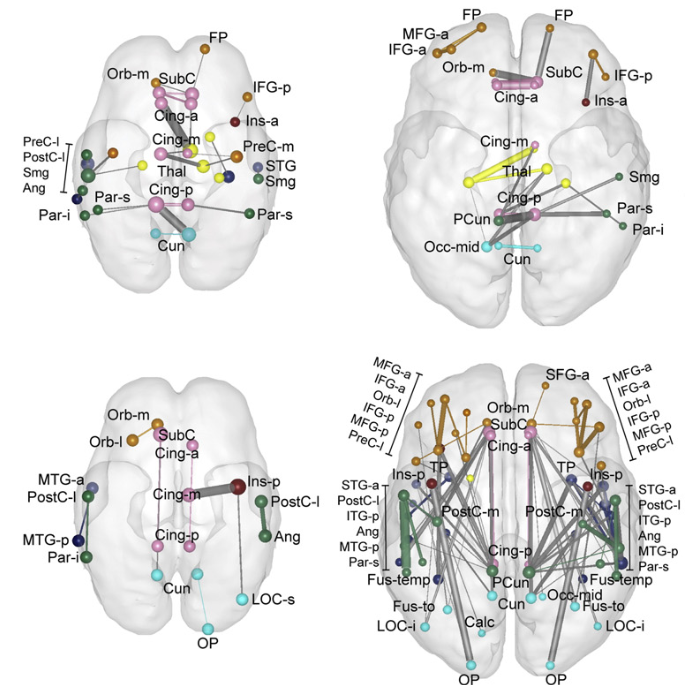
Fetal functional brain networks emerge during gestation following a stabled timing. Region-specific increase of functional signal synchrony followed a sequence of occipital (peak: 24.8 GW), temporal (peak: 26 GW), frontal (peak: 26.4 GW), and parietal expansion (peak: 27.5 GW). (Jakab et al. 2014)
The organization of structural connectivity an ts development in the fetal brain is discrupted by disease. Corpus callosum agenesis effects specific changes not only in the inter-hemispheric connections, but also within hemispheres. Each follows a characteristic timing. (Jakab et al. 2015)
Cortical expansion during fetal development can be modelled by comparing cortical surfaces across many individuals and linking their shape to gestaional age. We developed regularlization approaches that facilitate reliable estimates of development models. (Schwartz et al. 2016).
Development of the brain parenchymum proceeds in successive migrational waves of neuronal migration. The resulting laminar intensity profiles observable in both histology and in utero are indicative of developmental processes and important markers for neurodevelopmental diseases. We showed that the time-course of shifting patterns of laminar cortical structure can be modeled from fetal MRI.
Publications
- Stuempflen, M., Schwartz, E., Diogo, M. C., Glatter, S., Pfeiler, B., Kienast, P., ... & Kasprian, G. (2023). Fetal MRI based brain atlas analysis detects initial in utero effects of prenatal alcohol exposure. Cerebral Cortex, bhad005.
- Athena Taymourtash, Ernst Schwartz, Karl-Heinz Nenning, Daniel Sobotka, Roxane Licandro, Sarah Glatter, Mariana Cardoso Diogo, Polina Golland, Ellen Grant, Daniela Prayer, Gregor Kasprian, Georg Langs, Fetal development of functional thalamocortical and cortico–cortical connectivity, Cerebral Cortex, 2023; bhac446,
- Sobotka, D., Ebner, M., Schwartz, E., Nenning, K. H., Taymourtash, A., Vercauteren, T., Ourselin, S., Kasprian, G., Prayer, D., Langs, G., & Licandro, R. (2022). Motion Correction and Volumetric Reconstruction for Fetal Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data. NeuroImage, 119213.
- Fidon, F., Aertsen, M., Mufti, N., Deprest, T., Emam, D., Guffens, F., Schwartz, E., Ebner, M., Prayer, D., Kasprian, G., David, A., Melbourne, A., Ourselin, S., Deprest, J., Langs, G., Vercauteren, T. Distributionally Robust Segmentation of Abnormal Fetal Brain 3D MRI. in Proc of PIPPI 2021
- Schwartz, E., Diogo, M.C., Glatter, S., Seidl, R., Brugger, P.C., Gruber, G.M., Kiss, H., Nenning, K.H., IRC5 consortium, Langs, G. and Prayer, D., 2021. The Prenatal Morphomechanic Impact of Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum on Human Brain Structure and Asymmetry. Cerebral Cortex, 31(9), pp.4024-4037
- Kienast, P., Schwartz, E., Diogo, M. C., Gruber, G. M., Brugger, P. C., Kiss, H., Ulm, B., Bartha-Doering, L., Seidl, R., Weber, M. and Langs, G. & Kasprian, G. (2021). The Prenatal Origins of Human Brain Asymmetry: Lessons Learned from a Cohort of Fetuses with Body Lateralization Defects. Cerebral Cortex.
- Bartha-Doering, L., Schwartz, E., Kollndorfer, K., Fischmeister, F. P. S., Novak, A., Langs, G., Werneck H., Prayer D., Seidl R. & Kasprian, G. (2021). Effect of corpus callosum agenesis on the language network in children and adolescents. Brain Structure and Function, 1-13.
- E Schwartz, KH Nenning, G Kasprian, AL Schuller, L Bartha-Doering, G Langs. Multivarite Manifold Modeling of Functional Connectivity in Developing Language Networks. IPMI'17
- K.H. Nenning, H. Liuc, S. Ghoshd, M. Sabuncu, E. Schwartz, G. Langs. Diffeomorphic Functional Brain Surface Alignment: Functional Demons. to appear in NeuroImage (2017, in press)
- R. Licandro, K.-H. Nenning, E. Schwartz, K. Kollndorfer, L. Bartha-Doering, G. Langs. Changing Functional Connectivity in the Child's Developing Brain Affected by Ischaemic Stroke. Published in Proceedings of MICCAI 2016.
- E. Schwartz, G. Kasprian, A. Jakab, D. Prayer, V. Schöpf, and G. Langs. Modeling Fetal Cortical Expansion using Graph-Regularized Gompertz Models. Published in Proceedings of MICCAI 2016.
- E. Schwartz, G. Kasprian, A. Jakab, V. Schöpf, D. Prayer, and G. Langs. Spatio-Temporal Modelling of Laminar Neurodevelopment from Fetal MRI. MICCAI 2016 Workshop on Perinatal, Preterm and Paediatric Image analysis.
- V. Schöpf, G. Langs, A. Jakab. Functional Imaging of the Prenatal Brain. Fetal Development. Springer International Publishing, 2016. 429-437.
- D. Wang, R. L. Buckner, M. D. Fox, D. J. Holt, A. J. Holmes, S. Stoecklein, G. Langs, R. Pan, T. Qian, K. Li, J. T. Baker, S. M. Stufflebeam, K. Wang, X. Wang, B. Hong, and H. Liu, Parcellating cortical functional networks in individuals. Nature Neuroscience, advance online publication. pdf
- G. Langs, D. Wang, P. Golland, S. Mueller, R. Pan, M. Sabuncu, W. Sun, K. Li, H. Liu. Identifying Shared Brain Networks in Individuals by Decoupling Functional and Anatomical Variability. in Cerebral Cortex (in press)
- A Jakab, G Kasprian, E Schwartz, G Maria Gruber, C Mitter, D Prayer, V Schöpf, and G Langs. Disrupted developmental organization of the structural connectome in fetuses with corpus callosum agenesis. NeuroImage 111 (2015): 277-288.
- C. Schellen, E. Schwartz, G. M. Gruber, E. Mlczoch, M. Weber, B. Ulm, P. C. Brugger, G. Langs, U. Salzer-Muhar, D. Prayer, G. Kasprian. Fetal MRI detects early alterations of brain development in tetralogy of fallot. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology, 2015)
- C Mitter, A. Jakab, P.C. Brugger, G. Ricken, G. M. Gruber, D. Bettelheim, A. Scharrer, G. Langs, J.A. Hainfellner, D. Prayer and G. Kasprian. Validation of in utero tractography of human fetal commissural and internal capsule fibers with histological structure tensor analysis. In Frontiers in Neuroanatomy, 2015, doi: 10.3389/fnana.2015.00164
- Karl-Heinz Nenning, Kathrin Kollndorfer, Veronika Schöpf, Daniela Prayer, and Georg Langs. Multi-Subject Manifold Alignment of Functional Network Structures via Joint Diagonalization paper. in Advances in Information Processing in Medical Imaging, IPMI 2015.
- A Spatio-Temporal Latent Atlas for Semi-Supervised Learning of Fetal Brain Segmentations and Morphological Age Estimation. E. Dittrich, T. Riklin-Raviv, G. Kasprian, R. Donner, P. C. Brugger, D. Prayer, G. Langs. in Medical Image Analysis 14(1), pp.9-21, 2014.
- V. Schöpf, T. Schlegl, A. Jakab, G. Kasprian, R. Woitek, D. Prayer and G. Langs. The Relationship Between Eye Movement and Vision Develops Before Birth. in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience [pdf].
- Jakab A, Schwartz E, Kasprian G, Gruber GM, Prayer D, Schöpf V, Langs G. (2014) Fetal functional imaging portrays heterogeneous development of emerging human brain networks. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, (accepted manuscript doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00852).
- A locally linear method for enforcing temporal smoothness in serial image registration. [pdf] E. Schwartz, A. Jakab, G. Kasprian, L. Zoellei, and G. Langs. In Proc. of MICCAI STIA'14. LNCS 8682
- Advanced MRI techniques of the fetal brain. V. Schöpf, E. Dittrich, V. Berger-Kulemann, G. Kasprian, K. Kollndorfer, D. Prayer. Der Radiologe 2013, 53(2):136-140
Images: MUW/Bartha-Doering, MUW/Taymourtash, MUW/Sobotka, MUW/Jakab,
